|
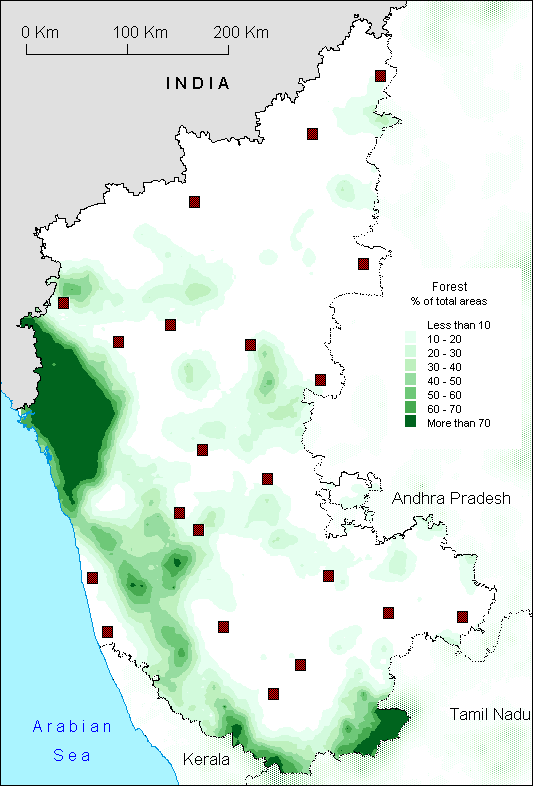
According to the State of the Forest Report 2001 (Forest Survey of India), Karnataka State has 37 000 kmē under forest cover, up to 19.39 % of the total land area. Of these, approx. 75% are under Reserve Forest, protected by the Karnataka Forest Department, 10% are Protected Forests (a deceptive name, since they are less protected than the Reserve Forest) and 15 % are Unclassified Forest.
The Reserve Forests forms a belt running almost continuously along the Western Ghats, from Belgaum to Mysore. Included in this belt are 5 National Parks and 23 Wildlife Sanctuaries, including the Bandipur Tiger Reserve and part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. The green patches easily seen on the map correspond either to one of the National Parks (Nagarhole and Bandipur bordering Kerala, Kudremukh up north along the WG) or to the Uttara Kanara District (bordering Goa), where Reserve Forest amounts to 70% of the district area. All those forests, including Muttodi forest in the Bababundangiri range are primarily deciduous forests.
Wet evergreen forests are located on the coastal belt and on the slopes of the Western Ghats. Both human pressure (plantations) and the presence of a lateritic cuirass are responsible for the degradation of those forests in the coast of South Kanara.
The forest of the eastern part of Uttara Kanara has been preserved for the area is unsuitable for plantations, and there are no big cities nearby. Yet, the recent development of cities like Yellapur and Sirsi caused a fast degradation of the forest cover in their vicinity. This trend seems to have been successfully brought to a standstill, but it shows how fast forest cover can vanish in the absence of a strong conservation policy. The Karnataka Forest Department has been taking strong conservation policies since early 80's (e.g. green tree felling ban), which partially explain the differences in forest cover with neighbouring Kerala.
Cl.G.
|